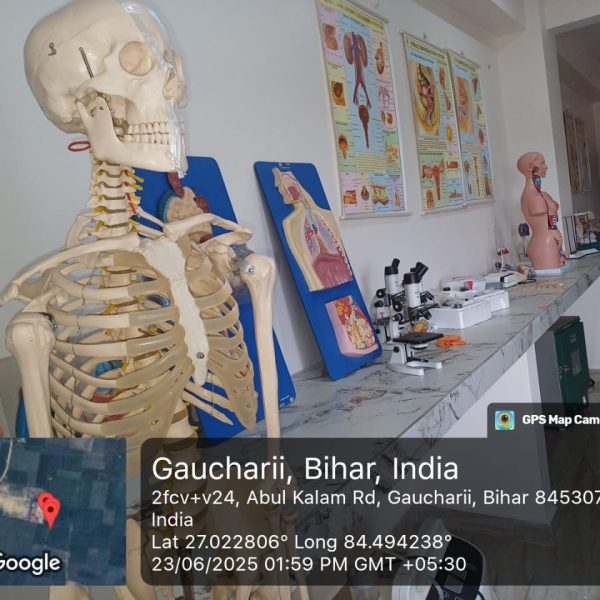
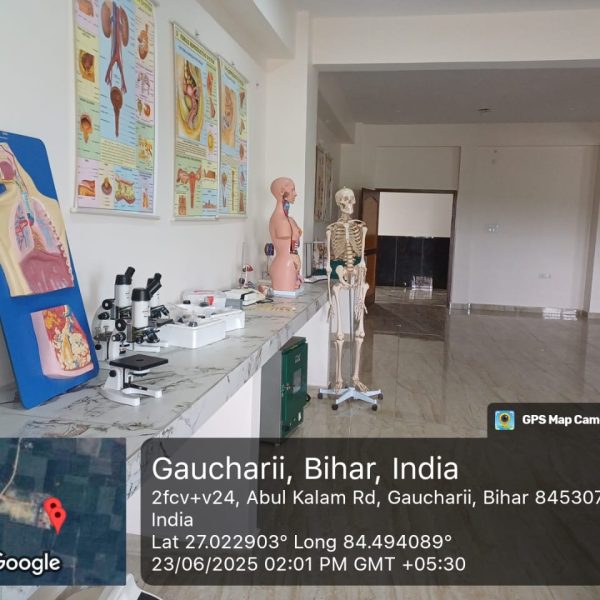
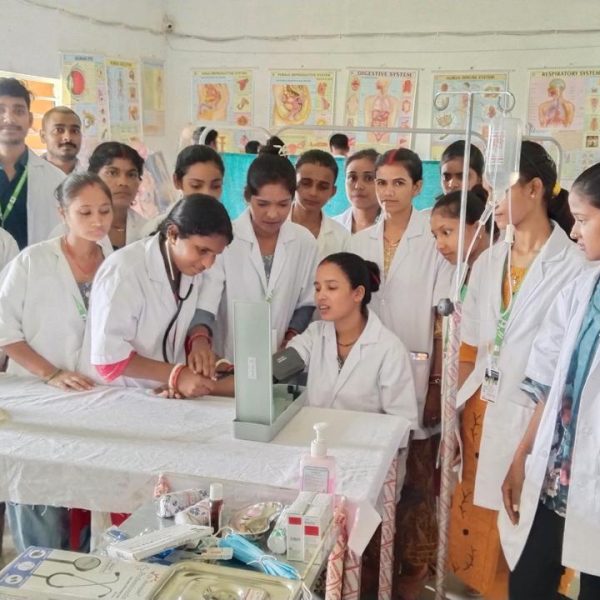
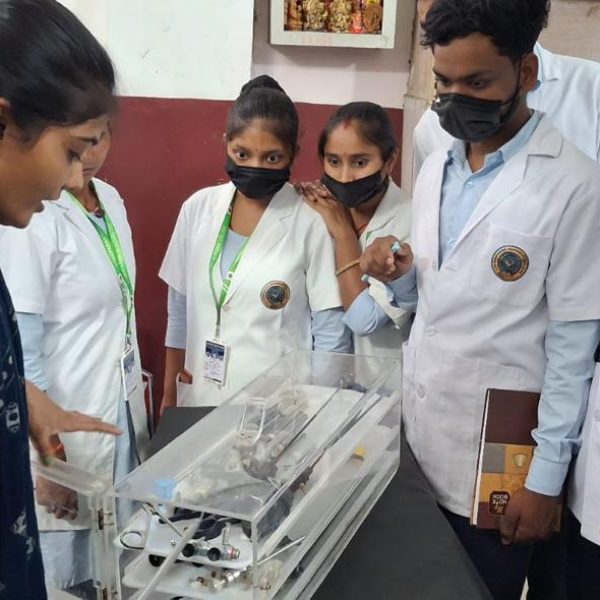
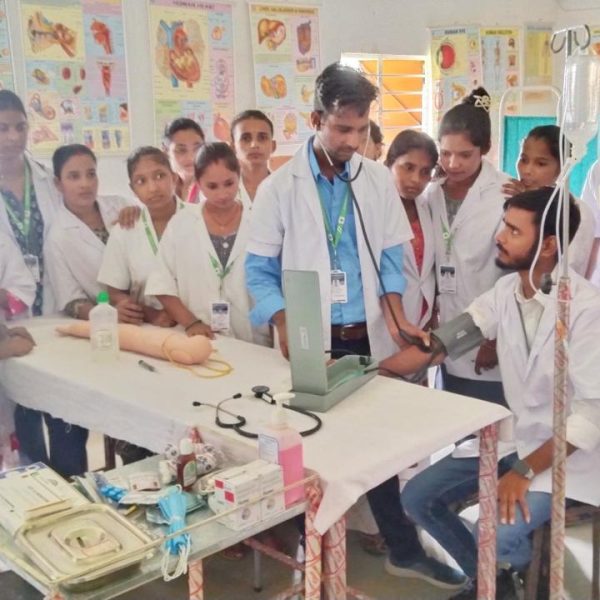
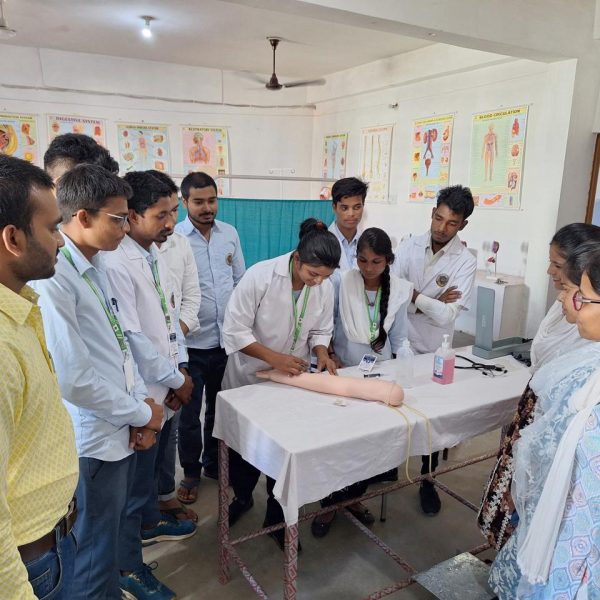
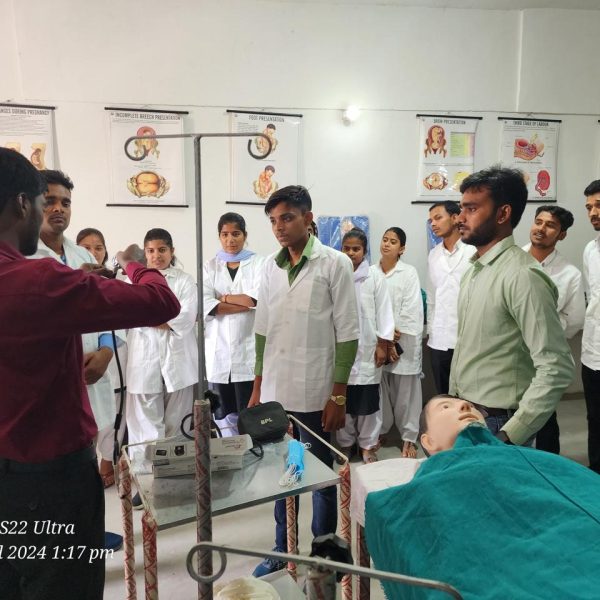






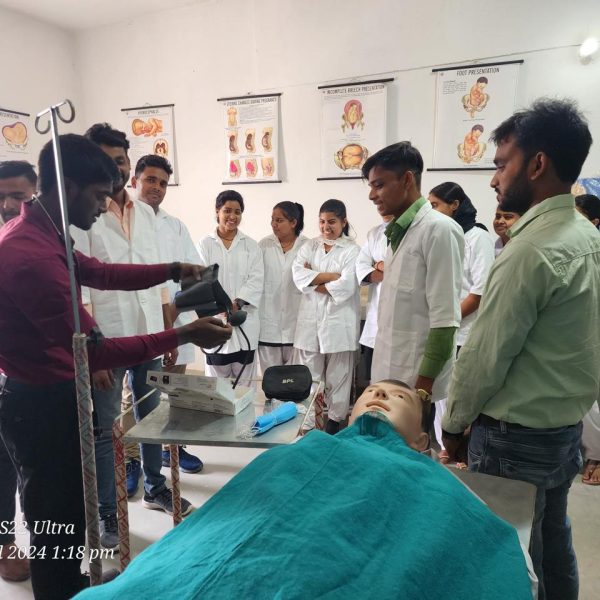

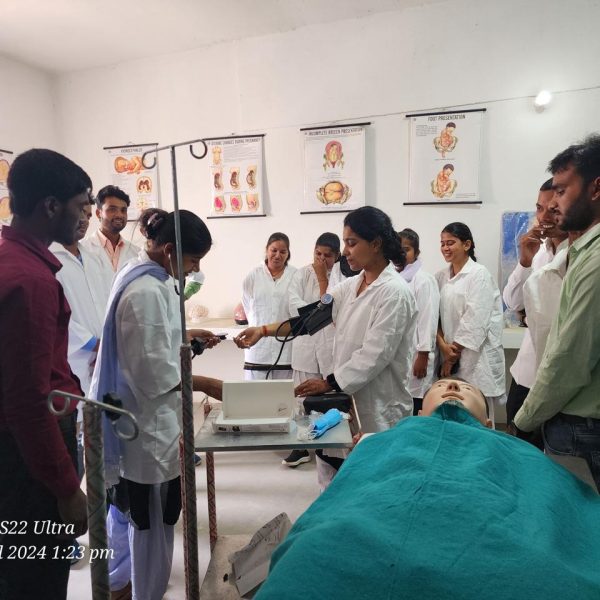
The purpose of a preclinical science lab in a nursing college is to provide nursing students with practical training and hands-on experience in basic science concepts that form the foundation of nursing practice. These labs are designed to teach fundamental principles in various scientific disciplines that are relevant to healthcare and nursing. The preclinical science lab serves several important purposes:
Anatomy and Physiology: Nursing students learn about the structure and function of the human body. They study various body systems and gain a deeper understanding of how these systems work together. This knowledge is crucial for comprehending the underlying mechanisms of health and disease.
Biology and Microbiology: Nursing students are introduced to essential concepts in biology, including cellular biology, genetics, and microbiology. Understanding these concepts helps students comprehend the origin and impact of diseases, infections, and the body’s response to them.
Chemistry and Biochemistry: Students learn about the principles of chemistry and biochemistry that are relevant to healthcare. This includes understanding drug interactions, metabolism, and the chemical basis of physiological processes.
Pathophysiology: Preclinical labs often introduce students to pathophysiology, which is the study of the functional changes that occur in the body due to diseases. This understanding is essential for identifying and managing health conditions.
Pharmacology: Students may be introduced to the basics of pharmacology, which involves learning about different drugs, their mechanisms of action, and their effects on the body. This knowledge helps nurses in medication administration and patient education.
Laboratory Skills: Preclinical labs also focus on developing essential laboratory skills, such as proper handling of laboratory equipment, performing basic tests, and analyzing data. These skills are valuable for clinical practice and research.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Engaging in hands-on activities and laboratory experiments helps students develop problem-solving and critical thinking skills, which are essential for making informed clinical decisions.
Safety and Ethical Practices: Preclinical science labs emphasize the importance of safety protocols, ethical considerations, and professionalism in scientific research and healthcare settings.
By incorporating a preclinical science lab in the nursing curriculum, nursing colleges aim to lay a strong scientific foundation for future nurses. This knowledge enhances their ability to provide evidence-based care, understand patient conditions, and collaborate effectively with other healthcare professionals. The lab experience helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, preparing nursing students for the complexities of real-world healthcare settings.
